Growth of Population and also changes of food consumption due to agricultural development, trade policies, urbanization, industrialization and others are causing increasing of water demand. Water should be available in adequate quantities and good quality. The effort to comply water demand for various needs is became an important issue especially in many developing countries. In around of the 1980, water supply in most of the developing countries were facing problems of quality and quantity. In 1990 many countries started to reform their water supply and sanitation service by involving private sector through scheme of public private partnerships (PPP).
Growth of Population and also changes of food consumption due to agricultural development, trade policies, urbanization, industrialization and others are causing increasing of water demand. Water should be available in adequate quantities and good quality. The effort to comply water demand for various needs is became an important issue especially in many developing countries. In around of the 1980, water supply in most of the developing countries were facing problems of quality and quantity. In 1990 many countries started to reform their water supply and sanitation service by involving private sector through scheme of public private partnerships (PPP).
In PPP, the government play important role in identifying the service needs of water supply, determine the desired output and convey a particular project to the private sector companies. Innovative strategies is needed by the private sector to ensure that they can complete the responsibilities in water supply service.
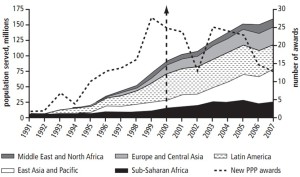
In the period of 1991 to 2000, the water supply served by private sectors in developing countries grew steadily from 6 million to 94 million. The population served by private water operators in developing and emerging countries has continued to increase steadily, from 94 million in 2000 to more than 160 million by the end of 2007. In 2007, private water operators from developing countries were serving about 67 million people (more than 40 percent of the market). There were more than 220 active water PPP in 41 developing and emerging countries (Marin, 2009).
Thus far, the PPP scheme in water supply increase rapidly in many developing countries. PPP’s success will produce a good value chain. Success of those scheme can be achieved through hard efforts because of the complexity of the scheme and future uncertainties in water demands and source availability. Improving the infrastructure and provide universal access is required as basic services in water supply. The role of local operators is very important because each country has their own constraint and different each others. The value chain of water supply is mainly composed of three parts (i) Sourcing, treatment and transmission, (ii) Distribution and (iii) Waste Water treatment (Aziz & Shah, 2012).
Selecting an appropriate strategy of private sector participation in form of management contracts is an important step and could be the key of success in the project identification stage. Detailed process of the strategy that includes exhaustive assessment of existing infrastructure, current performance on service delivery benchmarks, and the technical, operational and financial capability needs to be developed. Through PPP, private operators have improved operational efficiency, quality of service, area of coverage and access to water services.
References:
Aziz, A. & Shah, S.K. (2012). Public Private Partnerships in Urban Water Supply: Potential and Strategies. Chennai: Athena Infonomics India Pvt. Ltd
Marin, P. (2009). Public-Private Partnerships for Urban Water Utilities: A Review of Experiences in Developing Countries. Washington, DC: The World Bank.